OAuth2 Provider
Gitea supports acting as an OAuth2 Provider, allowing third-party applications to access its resources with user consent.
When acting as the OAuth2 Provider, Gitea verifies every authorization request against the related OAuth2 Application. This application can be set up by an individual user, an organization admin, or a Gitea instance admin.
Regardless of who configured the application, the first authorization attempt opens a new page in the user's web browser, prompting them to authorize the application.
Configuration
An OAuth2 Application in Gitea requires the following configuration made in two steps:
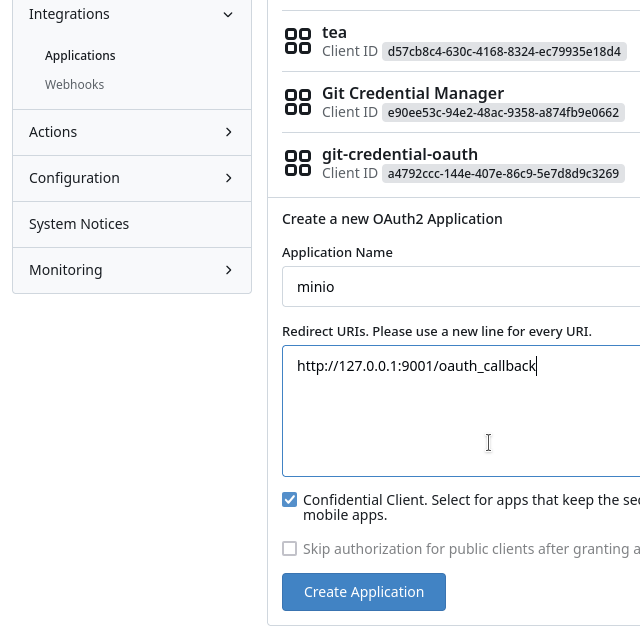
Gitea Step 1
- Name (
/admin/applications/) - Redirect URL (
/admin/applications/)
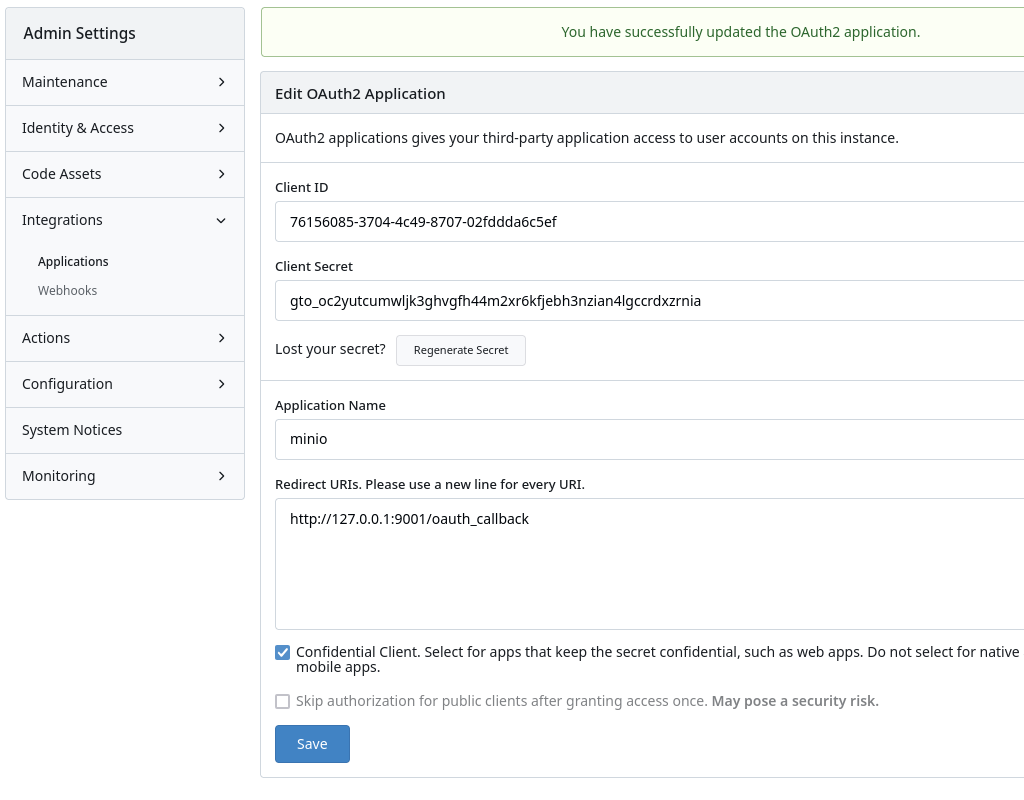
Gitea Step 2
- Client ID (
/admin/applications/oauth2/_id_) - Client Secret (
/admin/applications/oauth2/_id_) - Confidential client status (
/admin/applications/oauth2/_id_)
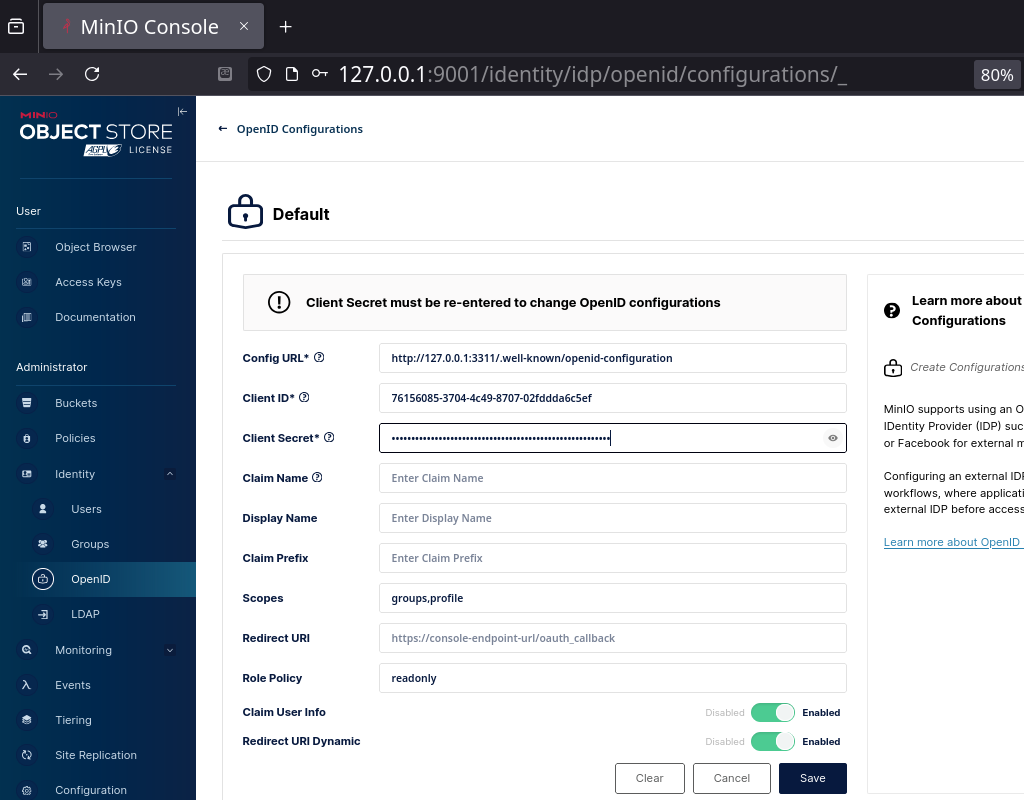
Third Party Step 3
The third-party (Relaying Parties) application's request must include:
- Credentials (Client ID and Client Secret)
- Desired scope and claims (expected to be provided by Gitea)
An example of MinIO:
Gitea's User Approval Step 3
For example, logging in with a Gitea account on MinIO...
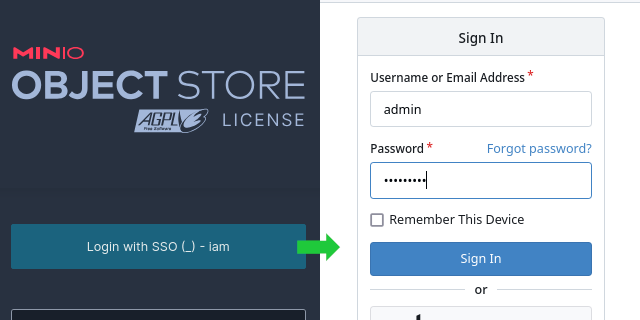
...will display the approval popup after a successful login:
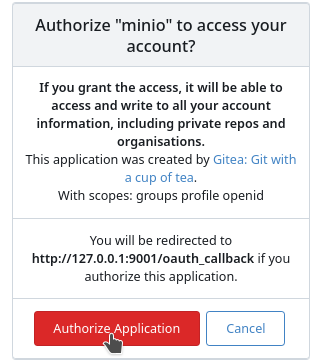
By default, if the third party sets the scopes to openid, email, profile, and groups, and the user approves, the application gains full access to all of the user's public and private resources (repositories, issues, user information, etc.).
NOTE: At present, an admin who sets up the OAuth2 Application in Gitea must rely on the scopes sent by the third party and an approval decision by the informed user if restrictive access is expected. There is no way for the admin to set restrictive access via scopes during the application setup process.
Granular Scopes
As of version v1.23, Gitea supports granular scopes, allowing third parties to request more limited access. These scopes, previously available only for Personal Access Tokens, enable users to restrict access to specific URL routes.
Scopes are grouped by high-level API routes and further refined as follows:
read:GETrouteswrite:POST,PUT,PATCH, andDELETEroutes (in addition toGET)
For example, a third party can request minimal access, allowing Gitea to act as a simple OpenID Connect (OIDC) Provider. If the third party adds only public-only to 'openid', no other or any combination of the scopes email, userinfo, or groups, Gitea will act as a basic Single Sign-On provider. This configuration provides only verification that the user can log in with the correct credentials, supplying only basic information such as username, email, and a list of public memberships in organizations and teams.
When any of the granular scopes known from Personal Access Tokens is introduced, Gitea will not allow full access (as it does by default). Instead, it will build granular access following read or write permissions to resources such as Repositories, Issues, ActivityPub, Admin functions, Organizations, Users, Packages, or miscellaneous features.
NOTE: If third party adds any scope other than the OIDC ones:
openid,profile, andgroupsor the ones found already in Personal Access Token the scope will fallback to full access as it was the case before v1.23
The approval page displayed to the user shows the list of scopes requested by the third party. Once approved, this decision is remembered. If the third party changes its requested scopes in future requests, the entire flow will fail, requiring re-authorization.
Endpoints
| Endpoint | URL |
|---|---|
| OpenID Connect Discovery | /.well-known/openid-configuration |
| Authorization Endpoint | /login/oauth/authorize |
| Access Token Endpoint | /login/oauth/access_token |
| Token Introspection Endpoint | /login/oauth/introspect |
| OpenID Connect UserInfo | /login/oauth/userinfo |
| JSON Web Key Set | /login/oauth/keys |
Supported OAuth2 Grants
At the moment Gitea only supports the Authorization Code Grant standard with additional support of the following extensions:
To use the Authorization Code Grant as a third party application it is required to register a new application via the "Settings" (/user/settings/applications) section of the settings. To test or debug you can use the web-tool https://oauthdebugger.com/.
Scopes
Gitea supports scoped access tokens, which allow users the ability to restrict tokens to operate only on selected url routes. Scopes are grouped by high-level API routes, and further refined to the following:
read:GETrouteswrite:POST,PUT,PATCH, andDELETEroutes (in addition toGET)
Gitea token scopes are as follows:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| (no scope) | Not supported. A scope is required even for public repositories. |
| activitypub | activitypub API routes: ActivityPub related operations. |
| read:activitypub | Grants read access for ActivityPub operations. |
| write:activitypub | Grants read/write/delete access for ActivityPub operations. |
| admin | /admin/* API routes: Site-wide administrative operations (hidden for non-admin accounts). |
| read:admin | Grants read access for admin operations, such as getting cron jobs or registered user emails. |
| write:admin | Grants read/write/delete access for admin operations, such as running cron jobs or updating user accounts. |
| issue | issues/*, labels/*, milestones/* API routes: Issue-related operations. |
| read:issue | Grants read access for issues operations, such as getting issue comments, issue attachments, and milestones. |
| write:issue | Grants read/write/delete access for issues operations, such as posting or editing an issue comment or attachment, and updating milestones. |
| misc | Reserved for future usage. |
| read:misc | Reserved for future usage. |
| write:misc | Reserved for future usage. |
| notification | notification/* API routes: user notification operations. |
| read:notification | Grants read access to user notifications, such as which notifications users are subscribed to and read new notifications. |
| write:notification | Grants read/write/delete access to user notifications, such as marking notifications as read. |
| organization | orgs/* and teams/* API routes: Organization and team management operations. |
| read:organization | Grants read access to org and team status, such as listing all orgs a user has visibility to, teams, and team members. |
| write:organization | Grants read/write/delete access to org and team status, such as creating and updating teams and updating org settings. |
| package | /packages/* API routes: Packages operations |
| read:package | Grants read access to package operations, such as reading and downloading available packages. |
| write:package | Grants read/write/delete access to package operations. Currently the same as read:package. |
| repository | /repos/* API routes except /repos/issues/*: Repository file, pull-request, and release operations. |
| read:repository | Grants read access to repository operations, such as getting repository files, releases, collaborators. |
| write:repository | Grants read/write/delete access to repository operations, such as getting updating repository files, creating pull requests, updating collaborators. |
| user | /user/* and /users/* API routes: User-related operations. |
| read:user | Grants read access to user operations, such as getting user repo subscriptions and user settings. |
| write:user | Grants read/write/delete access to user operations, such as updating user repo subscriptions, followed users, and user settings. |
Pre-configured Applications
Gitea creates OAuth applications for the following services by default on startup, as we assume that these are universally useful.
| Application | Description | Client ID |
|---|---|---|
| git-credential-oauth | Git credential helper | a4792ccc-144e-407e-86c9-5e7d8d9c3269 |
| Git Credential Manager | Git credential helper | e90ee53c-94e2-48ac-9358-a874fb9e0662 |
| tea | tea | d57cb8c4-630c-4168-8324-ec79935e18d4 |
To prevent unexpected behavior, they are being displayed as locked in the UI and their creation can instead be controlled by the DEFAULT_APPLICATIONS parameter in app.ini.
Client types
Gitea supports both confidential and public client types, as defined by RFC 6749.
For public clients, a redirect URI of a loopback IP address such as http://127.0.0.1/ allows any port. Avoid using localhost, as recommended by RFC 8252.
Examples
Confidential client
This example does not use PKCE.
-
Redirect the user to the authorization endpoint in order to get their consent for accessing the resources:
https://[YOUR-GITEA-URL]/login/oauth/authorize?client_id=CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&response_type=code&state=STATEThe
CLIENT_IDcan be obtained by registering an application in the settings. TheSTATEis a random string that will be sent back to your application after the user authorizes. Thestateparameter is optional, but should be used to prevent CSRF attacks.
The user will now be asked to authorize your application. If they authorize it, the user will be redirected to the
REDIRECT_URL, for example:https://[REDIRECT_URI]?code=RETURNED_CODE&state=STATE -
Using the provided
codefrom the redirect, you can request a new application and refresh token. The access token endpoint accepts POST requests withapplication/jsonandapplication/x-www-form-urlencodedbody, for example:POST https://[YOUR-GITEA-URL]/login/oauth/access_token{
"client_id": "YOUR_CLIENT_ID",
"client_secret": "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET",
"code": "RETURNED_CODE",
"grant_type": "authorization_code",
"redirect_uri": "REDIRECT_URI"
}Response:
{
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJnbnQiOjIsInR0IjowLCJleHAiOjE1NTUxNzk5MTIsImlhdCI6MTU1NTE3NjMxMn0.0-iFsAwBtxuckA0sNZ6QpBQmywVPz129u75vOM7wPJecw5wqGyBkmstfJHAjEOqrAf_V5Z-1QYeCh_Cz4RiKug",
"token_type": "bearer",
"expires_in": 3600,
"refresh_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJnbnQiOjIsInR0IjoxLCJjbnQiOjEsImV4cCI6MTU1NzgwNDMxMiwiaWF0IjoxNTU1MTc2MzEyfQ.S_HZQBy4q9r5SEzNGNIoFClT43HPNDbUdHH-GYNYYdkRfft6XptJBkUQscZsGxOW975Yk6RbgtGvq1nkEcklOw"
}The
CLIENT_SECRETis the unique secret code generated for this application. Please note that the secret will only be visible after you created/registered the application with Gitea and cannot be recovered. If you lose the secret, you must regenerate the secret via the application's settings.The
REDIRECT_URIin theaccess_tokenrequest must match theREDIRECT_URIin theauthorizerequest. -
Use the
access_tokento make API requests to access the user's resources.
Public client (PKCE)
PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange) is an extension to the OAuth flow which allows for a secure credential exchange without the requirement to provide a client secret.
Note: Please ensure you have registered your OAuth application as a public client.
To achieve this, you have to provide a code_verifier for every authorization request. A code_verifier has to be a random string with a minimum length of 43 characters and a maximum length of 128 characters. It can contain alphanumeric characters as well as the characters -, ., _ and ~.
Using this code_verifier string, a new one called code_challenge is created by using one of two methods:
- If you have the required functionality on your client, set
code_challengeto be a URL-safe base64-encoded string of the SHA256 hash ofcode_verifier. In that case, yourcode_challenge_methodbecomesS256. - If you are unable to do so, you can provide your
code_verifieras a plain string tocode_challenge. Then you have to set yourcode_challenge_methodasplain.
After you have generated this values, you can continue with your request.
-
Redirect the user to the authorization endpoint in order to get their consent for accessing the resources:
https://[YOUR-GITEA-URL]/login/oauth/authorize?client_id=CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&response_type=code&code_challenge_method=CODE_CHALLENGE_METHOD&code_challenge=CODE_CHALLENGE&state=STATEThe
CLIENT_IDcan be obtained by registering an application in the settings. TheSTATEis a random string that will be sent back to your application after the user authorizes. Thestateparameter is optional, but should be used to prevent CSRF attacks.
The user will now be asked to authorize your application. If they authorize it, the user will be redirected to the
REDIRECT_URL, for example:https://[REDIRECT_URI]?code=RETURNED_CODE&state=STATE -
Using the provided
codefrom the redirect, you can request a new application and refresh token. The access token endpoint accepts POST requests withapplication/jsonandapplication/x-www-form-urlencodedbody, for example:POST https://[YOUR-GITEA-URL]/login/oauth/access_token{
"client_id": "YOUR_CLIENT_ID",
"code": "RETURNED_CODE",
"grant_type": "authorization_code",
"redirect_uri": "REDIRECT_URI",
"code_verifier": "CODE_VERIFIER",
}Response:
{
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJnbnQiOjIsInR0IjowLCJleHAiOjE1NTUxNzk5MTIsImlhdCI6MTU1NTE3NjMxMn0.0-iFsAwBtxuckA0sNZ6QpBQmywVPz129u75vOM7wPJecw5wqGyBkmstfJHAjEOqrAf_V5Z-1QYeCh_Cz4RiKug",
"token_type": "bearer",
"expires_in": 3600,
"refresh_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJnbnQiOjIsInR0IjoxLCJjbnQiOjEsImV4cCI6MTU1NzgwNDMxMiwiaWF0IjoxNTU1MTc2MzEyfQ.S_HZQBy4q9r5SEzNGNIoFClT43HPNDbUdHH-GYNYYdkRfft6XptJBkUQscZsGxOW975Yk6RbgtGvq1nkEcklOw"
}The
REDIRECT_URIin theaccess_tokenrequest must match theREDIRECT_URIin theauthorizerequest. -
Use the
access_tokento make API requests to access the user's resources.